# 双向数据绑定原理
双向绑定的核心:Object.defineProperty() 和 数据的发布订阅。
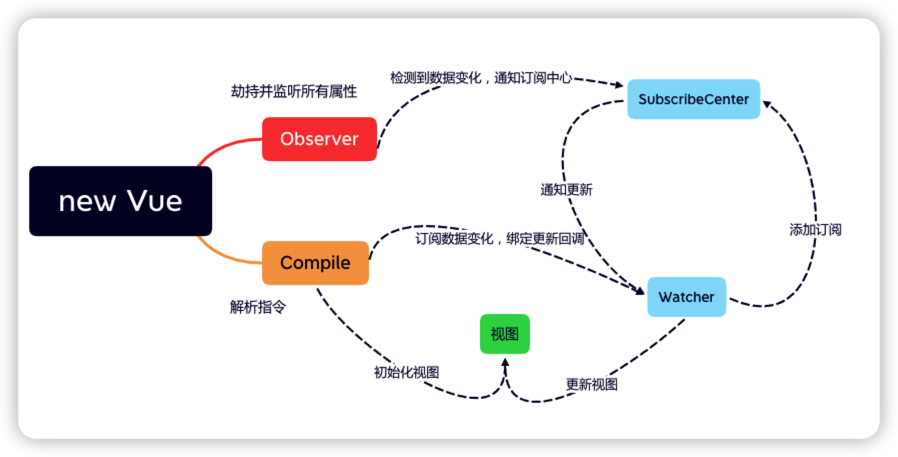
- 1、当我们new Vue时候,做了两件大事,劫持data上的数据和执行解析指令;
- 2、劫持数据的目的是 当数据更新,即发生set的时候,通知订阅中心进行更新逻辑,并更新视图;
- 3、解析指令,
- (1)、做视图的初始化,将图中的插值或者变量替换成对应的数据;
- (2)、生成Watcher,订阅来自变量的数据变化。
- 4、当数据改变时,Observer监听到数据变化,通知订阅中心,订阅中心通知对所有订阅者进行视图更新。
接下来一步步看这个过程:
# 1、初始化
class Vue {
constructor(obj_instance) {
this.$el = document.querySelector(obj_instance.el)
this.$data = obj_instance.data || {};
Observer(this.$data);
Compile(this);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
这里只做了数据劫持和页面解析。
# 2、数据劫持 Observer
function Observer(data_instance) {
Object.keys(data_instance).forEach((key) => {
let value = data_instance[key];
if (!data_instance || typeof data_instance !== 'object') {
return;
}
Observer(value);
Object.defineProperty(data_instance, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
return value;
},
set(newValue) {
value = newValue;
subscribeCenter.notify();
Observer(newValue);
}
})
})
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
- 1、遍历data下所有属性,进行属性劫持;(Object.defineProperty);
- 2、对于对象属性进行递归遍历;(这里只考虑对象,数组增加判断递归遍历即可)
- 3、关于数据劫持,getter只是取到value,需要注意的是:这里的value需要提前利用闭包缓存;
- 4、setter中除了设置新值,还有通知订阅中心数据更新,对于新值需要进行递归监听,防止数据结构发生变化。
# 3、编译指令 Compile
function Compile(vm) {
const fragment = document.createDocumentFragment();
let child;
while (child = vm.$el.firstChild) {
fragment.append(child);
}
fragment_compile(fragment);
function fragment_compile(node) {
if (node.nodeType === 3) {
replaceField(node, vm);
} else if (node.nodeType === 1) {
const attr = Array.from(node.attributes);
attr.forEach(a => {
if (a.nodeName === 'v-model') {
node.value = getValue(vm.$data, a.nodeValue);
new Watcher(vm, a.nodeValue, (newValue) => {
node.value = newValue
});
node.addEventListener('input', (event) => {
assignment(vm.$data, a.nodeValue, event.target.value)
})
}
})
}
node.childNodes.forEach(c => {
fragment_compile(c);
})
}
vm.$el.appendChild(fragment);
}
function replaceField(node, vm) {
const originNodeValue = node.nodeValue;
const pattern = /\{\{\s*(\S+)\s*\}\}/;
const result_regex = pattern.exec(originNodeValue);
if (result_regex) {
const key = result_regex[1];
const value = getValue(vm.$data, result_regex[1])
node.nodeValue = originNodeValue.replace(pattern, value);
new Watcher(vm, key, (newValue) => {
node.nodeValue = originNodeValue.replace(pattern, newValue);
});
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
- 1、将页面元素存放于文档碎片进行操作,有子元素的元素递归处理,完成操作后,一次性更新到视图;提升性能
- 2、文本节点的处理
- (1)、变量替换;
- (2)、新建watcher并添加到订阅中心(在Watcher中);
- 3、元素节点的处理;
- (1)、v-model 元素进行变量替换
- (2)、新建watcher并添加到订阅中心(在Watcher中)
- (3)、添加 input 时间监听,更新值到data,这里会触发数据更新发布。
# 4、订阅中心
let subscribeCenter = null;
function createDepInstance() {
if (!subscribeCenter) {
subscribeCenter = new SubscribeCenter();
}
}
// 依赖 - 订阅中心
class SubscribeCenter {
constructor() {
this.subscribes = [];
}
addSub(sub) {
this.subscribes.push(sub);
}
notify() {
this.subscribes.forEach(sub => sub.update());
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
- 1、addSub:添加订阅
- 2、notify:发布者通知数据更新,更新订阅者;
# 5、订阅者
class Watcher {
constructor(vm, key, callback) {
this.vm = vm;
this.key = key;
this.callback = callback;
this.subscribe();
}
update() {
this.value = getValue(vm.$data, this.key);
this.callback(this.value);
}
subscribe() {
createDepInstance();
subscribeCenter.addSub(this);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
- 1、update: 更新视图
- 2、subscribe:添加到订阅中心
# 6、工具函数
// obj = {more: {like: '999'}}
// 获取复杂结构数据 如: more.like
function getValue(obj, keyStr) {
const keys = keyStr.split('.');
return keys.reduce((res, key) => res[key], obj);
}
// 为复杂数据结构数据赋值:more.like
function assignment(obj, key, value) {
const keys = key.split('.');
const len = keys.length;
if (len === 1) {
obj[key] = value;
} else {
const tempObj = keys.slice(0, len - 1).reduce((res, k) => res[k], obj);
tempObj[keys[len - 1]] = value;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
